Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
UV curing technology has revolutionized various industries. The "Uv Curing Light Source" plays a vital role in this process. According to a recent report by Research and Markets, the global UV curing market is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.4%.
UV curing involves using ultraviolet light to initiate a photochemical reaction, solidifying inks, coatings, and adhesives. This method offers several advantages, such as faster curing times and reduced VOC emissions. However, the effectiveness of a UV curing system is heavily reliant on the specifications of its light source. Inadequate light intensity or improper wavelength can lead to insufficient curing and compromised product quality.
While UV curing techniques have been broadly adopted, some challenges remain. Concerns about the potential health risks associated with UV exposure persist. Furthermore, not all materials respond equally to UV light. It's essential for manufacturers to carefully select their UV curing light source to achieve optimal results. As industries continue to evolve, ongoing research will be crucial to address these challenges.
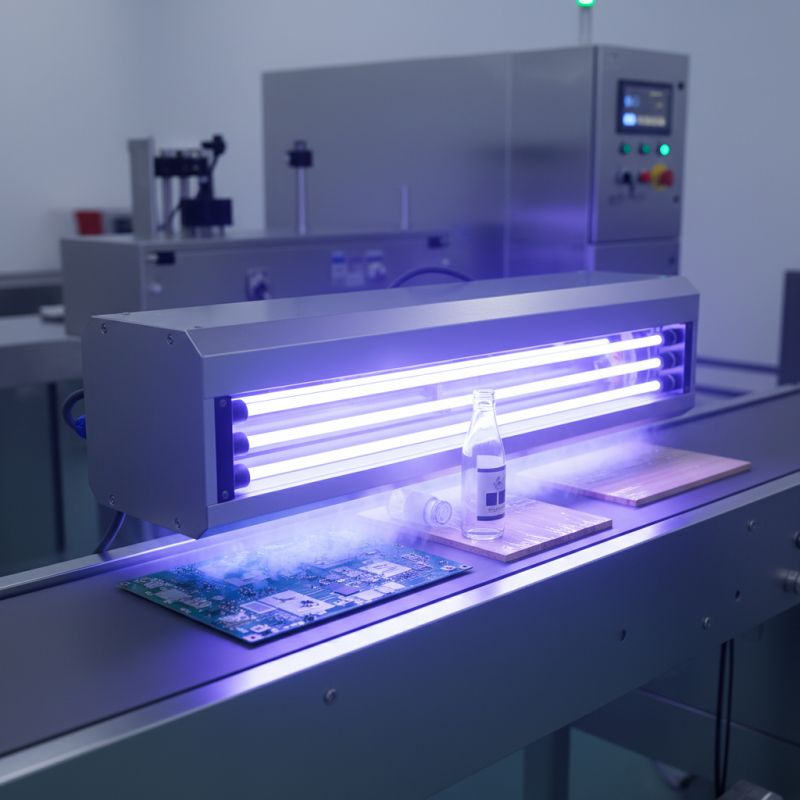

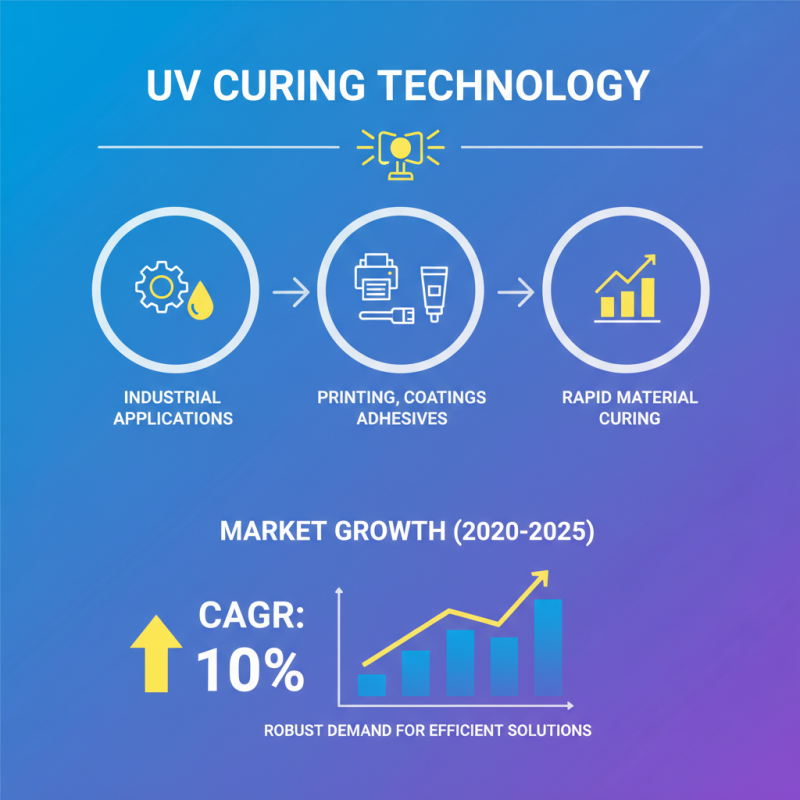
UV curing light sources are essential in various industrial applications. They emit ultraviolet light to cure materials quickly. This technology is prevalent in industries like printing, coatings, and adhesives. According to a market report, the UV curing market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% from 2020 to 2025. This growth signals a robust demand for efficient curing solutions.
The mechanism of UV curing involves photochemical reactions. When UV light hits specially formulated inks or coatings, it initiates a chemical reaction. This reaction causes the material to harden almost instantly. Companies also use UV light for various applications. However, it's crucial to ensure proper safety measures are in place. Prolonged exposure to UV light can pose health risks. Balancing efficiency with safety is vital.
Challenges remain in the UV curing process. Not all materials respond well to UV light, limiting its application. Additionally, the energy consumption related to UV systems can be significant. Developing more energy-efficient solutions is an ongoing concern. Industry stakeholders continually evaluate these challenges to enhance the effectiveness of UV curing technologies.
UV curing light sources come in various types, each designed for specific applications. One common type is the mercury vapor lamp. These lamps emit a broad spectrum of UV light, making them effective for curing inks and coatings. They are widely used in the printing industry. However, they can generate heat, which might affect sensitive materials.
Another popular option is LED UV lamps. They are energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan. These lamps produce less heat and can cure thicker materials without damage. Industries such as electronics and automotive often prefer LED lamps. Yet, there can be challenges with certain UV-sensitive formulas.
Lastly, there are pulsed xenon lamps. These provide powerful bursts of UV light and can cure materials rapidly. They are useful in high-speed applications, such as packaging. However, their cost and complexity can be a drawback for smaller operations.
Each light source has its strengths and weaknesses. It is essential to choose the right one based on the specific requirements of your project. Consider the material being used and the desired curing speed to make an informed decision.
UV curing is a highly efficient process that converts liquid materials into solid forms using ultraviolet light. This technology is widely used in various industries, such as printing, coatings, and adhesives. The science behind UV curing is based on photopolymerization. When exposed to UV light, photoinitiators in the resin absorb energy and generate free radicals, leading to a rapid polymerization reaction. This process can occur in mere seconds, creating a robust final product.
Research shows that UV curing can increase productivity by 30-50% compared to traditional curing methods. This efficiency is appealing to manufacturers looking to streamline operations. However, not all materials cure effectively under UV light. Each formulation may require specific wavelengths and intensity levels for optimal results. It’s essential to test and refine materials before full-scale application to avoid costly errors.
Tips: Always review the UV spectrum of your curing light. Mismatched wavelengths may result in incomplete curing and poor adhesion. Also, consider the environmental factors, like temperature and humidity, as they can impact curing efficiency. A little adjustment can make a substantial difference in the end product's quality. Experimentation is key to finding the perfect balance in the curing process.
UV curing light sources offer several advantages across various industries. They are primarily used in coatings, adhesives, and printing. The process is quick, and it provides durable finishes. Products cured under UV light are often more resistant to scratches and chemicals. This leads to longer-lasting applications, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
One notable benefit is the energy efficiency of UV curing. Traditional drying methods require significant energy and time. In contrast, UV light cures materials almost instantly. This speed improves production rates. However, it can be challenging for some manufacturers to adapt to this technology. Training staff and adjusting processes take time and investment.
Moreover, UV curing produces minimal waste. It requires fewer solvents compared to traditional methods, making it more environmentally friendly. However, the initial setup costs can be a barrier for some companies. The efficiency of these systems could lead to overproduction if not managed properly. Therefore, careful planning is essential to maximize the benefits while minimizing potential downsides.
UV curing light sources are widely used in various industries for their efficiency. However, safety must be a priority when using these powerful tools. UV light exposure can lead to skin burns and eye injuries. Research suggests that even short exposure can cause acute damage. A report from the International Agency for Research on Cancer highlighted the risks associated with UV radiation.
When working with UV curing systems, wear appropriate protective equipment. This includes goggles that filter UV light and protective clothing. Proper ventilation also plays a crucial role. Ensure workspaces are well-ventilated to minimize inhalation risks from emitted substances. Avoid skin contact with uncured adhesives or inks, as they may contain harmful chemicals.
Tip: Regular safety training for users of UV curing systems can enhance awareness. Schedule periodic reviews of safety protocols to address any overlooked risks. It’s essential to cultivate a safety-first culture in the workspace. Take the time to reflect on past incidents for continuous improvement. By doing so, you can better protect yourself and your team while reaping the benefits of UV technology.
| Feature | Description | Safety Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source Type | UV LED, Mercury Vapor | Use protective eyewear and skin protection when operating. |
| Wavelength Range | 200 - 400 nm | Avoid direct skin exposure; use UV-blocking barriers. |
| Curing Speed | Rapid curing of inks, adhesives, and coatings | Ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhalation of fumes. |
| Applications | Industrial printing, automotive, electronics | Follow material safety data sheets for UV materials. |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning of light sources, check for damage | Disconnect power before maintenance; inspect for leaks. |